Diagnostics, replacement of faulty elements, commissioning, adjustments and tests after the repair are a typical set of activities carried out during service repairs. All of them require appropriate, specialized tools, which should be characterized by high durability and small dimensions.
Due to the variety of technologies used for the assembly of electronic circuits – from simple assembly of the elements to be soldered onto single-sided plates, through the technology of multilayer plates with metallized holes, to surface assembly – the efficient and safe removal of defective elements requires the use of specialized equipment. Above all, the risk of damage to the surface and adjacent elements must be excluded. Until recently, it was possible to try to dismantle components with standard soldering irons, but due to the ever smaller spacing between the outlets and the ever smaller dimensions of housings this type of operation is more and more often condemned to failure.
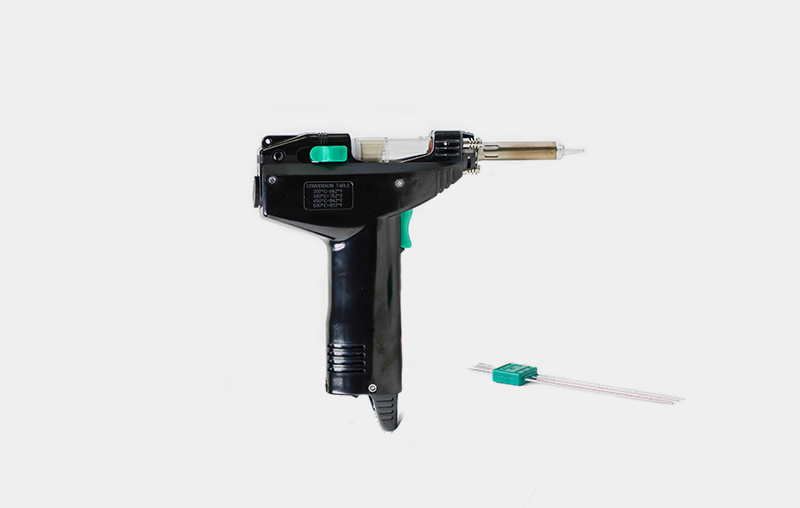
The DEN-ON SC 7000Z is a tool for dismantling electronic components, offering great versatility. Its most important feature, which determines its exceptional usability, is its unique design, consisting in the use of an integrated compressor while maintaining exemplary ergonomics. It is its lightness and portability that makes it particularly suitable for work in field conditions, i.e. in the place where the equipment under repair is used.
The built-in compressor and the possibility of changing the desoldering tool so that the process of heating the soldering point and removing tin is optimal for a given type of element, surface and mounting technology used are the basis of the outstanding functionality of this device. The tool can work with several types of suction nozzles – they enable quick and clean disassembly of the THT elements from boards containing up to twelve layers with metallized holes. By equipping the tool with a blowing nozzle and switching the compressor operation mode, it is possible to dismantle all systems made in SMT technology using the hot air blowing method.
A suitable set including nozzle, wire and steel band with grippers, as well as a blowing filter, is offered by the manufacturer as an option. The disassembly of the components in PLCC and PQFP housings is facilitated by the optional, specialized blast heads. They heat up and free the leads of the components at the same time, and the compressor operates the suction cup, which lifts the removed element when the tin reaches a liquid state (but this does not happen automatically – the operation of the suction cup is initiated by the operator). During operation in the “classic” mode, i.e. with a suction nozzle, the removed solder is collected in a tank equipped with a filter. The tank must be emptied gradually, the filter is replaced when its contamination reduces the suction power.
The use of the desoldering tool is simple and convenient. The desired temperature of 350…500°C is set with the knob. In order to remove the solder surrounding the tip of the component to be disassembled, it is inserted into the opening of the working nozzle, gently pressing the nozzle against the surface of the board as the solder melts. When the compressor is turned on at the right time, the solder is sucked out of the board surface and the element’s foot is released from the hole.
Dismantling of SMD elements by hot air blowing is as follows: after installing the appropriate nozzle, set the compressor mode and setting the temperature (usually 450…500°C), put the nozzle outlet at a distance of 1…2 cm from the element to be removed, start the compressor and, by circular movements, heat the element and the plate around it, then by pushing the nozzle to the outlets, the binder is melted and the element can be held and lifted with tweezers.
The disassembly of integrated circuits requires the use of a steel wire or strip installed in a special gripper. The process involves heating up the soldering points and releasing the subsequent legs by moving the tape between them and the ground. As mentioned, the disassembly of PLCC and PQFP circuits is more efficient by using special heads, acting on the leads along the entire circumference of the element. To work in this mode, the compressor is set to suction, but this time it will not be used to remove the solder, but to lift the component to be dismantled using a suction cup located centrally in the head.
The temperature is set in this case slightly higher (50…120°C depending on the head dimensions) than the expected working temperature of the head edge. After heating up, the edges of the head are coated with tin to ensure efficient and even heat transfer. Then, with some movement, place the head on the component leads, pressing lightly as the solder melts, and finally turn on the compressor and lift the tool with the soldered element. The spring installed inside the head moves the element away from the hot edges, eliminating the possibility of its overheating – it may happen, after all, that the desoldered element is in good working order, so one should make sure that the risk of damage preventing its re-use is reduced. All professional activities should be above all effective and safe. The quality and technical capabilities of the tools used are one of the most important factors influencing this. Some tools still have the property of making work more enjoyable – these include the SC 7000Z.